The Endocannabinoid System
How It Works
The Role of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) in Regulating Bodily Functions
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a natural part of the body that oversees all the underlying systems, including the immune, nervous and digestive systems. It is important to maintain homeostasis within this system. as without such balance, the body will not function at it’s best. (Homeostasis means that all systems are stable and balanced) Instability within a single system may create issues in others, essentially throwing in a monkey wrench and damaging the whole body.
The Role of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) in Regulating Bodily Functions
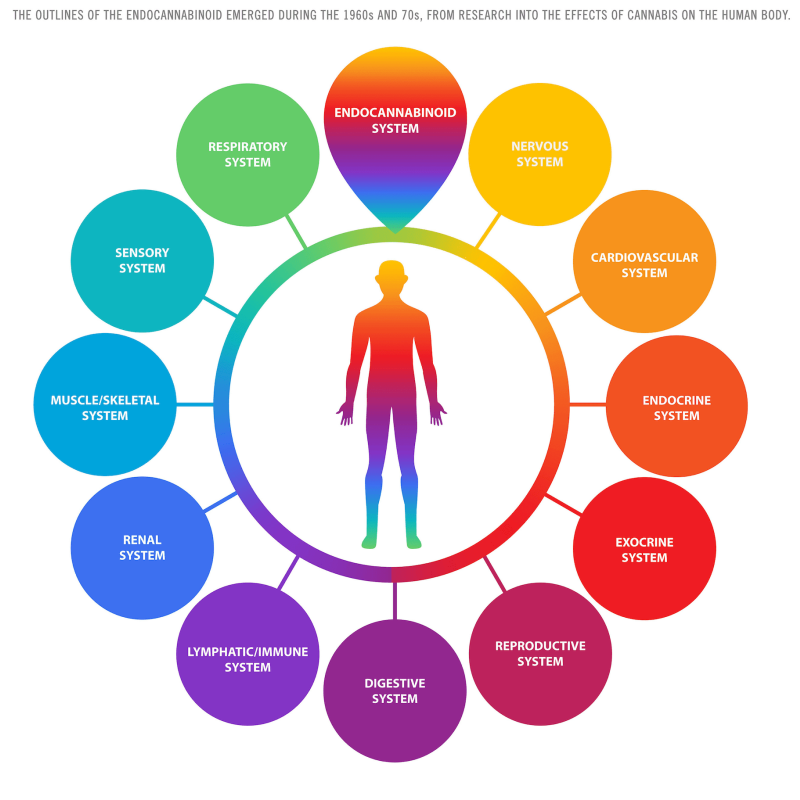
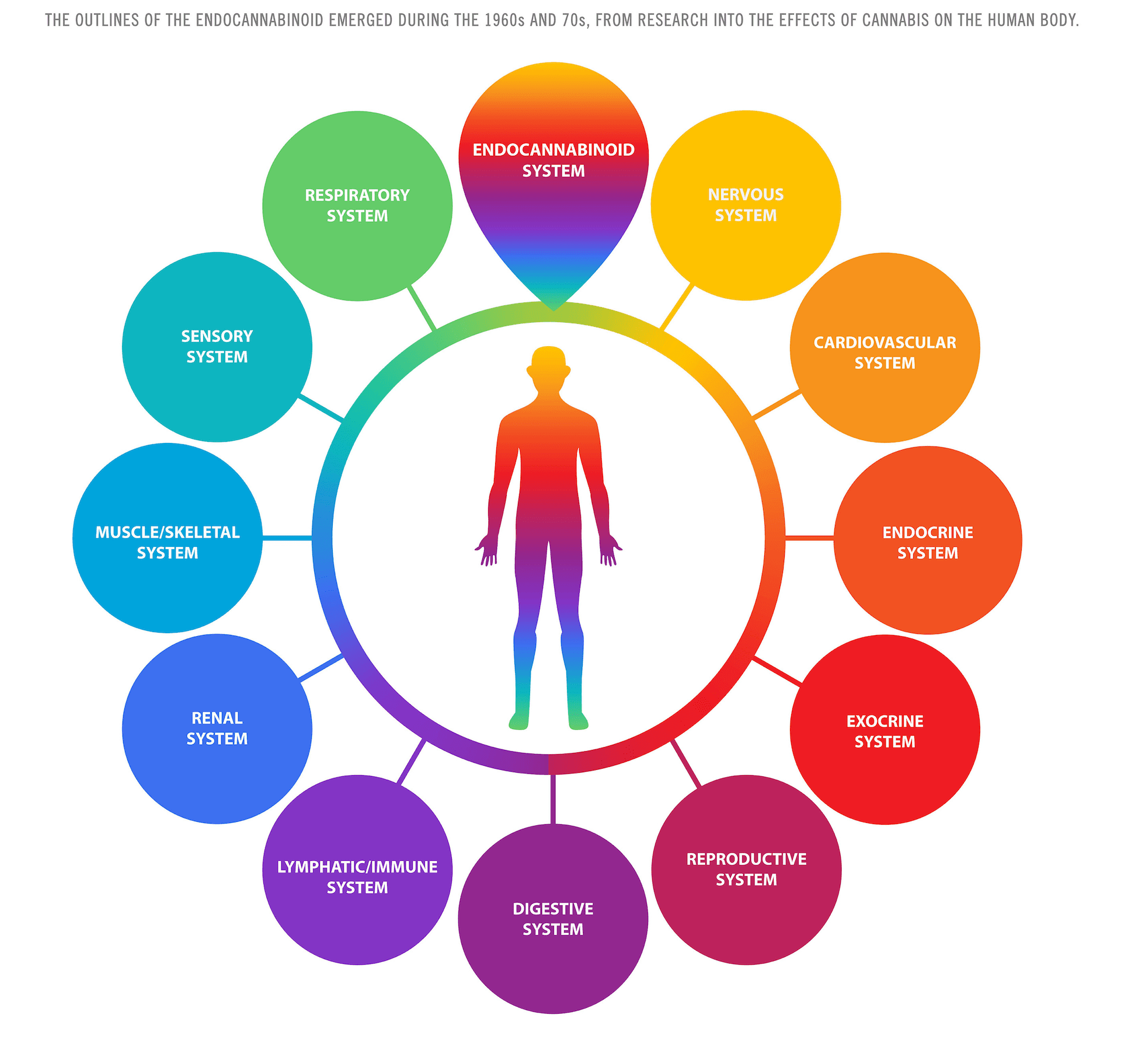
This diagram represents the interaction between the human body’s various systems and the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS, discovered during the 1960s and 70s in research on cannabis, plays a role in regulating and balancing different bodily functions. Each of the human body systems shown in the outer circle interacts with the ECS in some capacity, highlighting its broad influence on overall health.
Here’s an overview of the systems connected to the ECS in this diagram:
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS) – Central part of the diagram, influencing a wide range of bodily processes.
- Nervous System – ECS influences brain function, mood regulation, and neurological processes.
- Cardiovascular System – ECS impacts heart rate, blood pressure, and vascular health.
- Endocrine System – ECS helps regulate hormone production and balance.
- Exocrine System – ECS affects glands that produce sweat, saliva, and other secretions.
- Reproductive System – ECS plays a role in fertility, reproductive health, and sexual function.
- Digestive System – ECS influences digestion, appetite, and metabolism.
- Lymphatic/Immune System – ECS helps regulate immune responses, including inflammation.
- Renal System – ECS impacts kidney function and fluid balance in the body.
- Muscle/Skeletal System – ECS plays a role in muscle function and bone health.
- Sensory System – ECS affects how the body processes sensory input, such as pain or temperature.
- Respiratory System – ECS may help modulate breathing and lung function.
The ECS acts as a regulatory mechanism that helps maintain homeostasis across these diverse systems, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Watch a Video on this Topic
The Endocannabinoid System
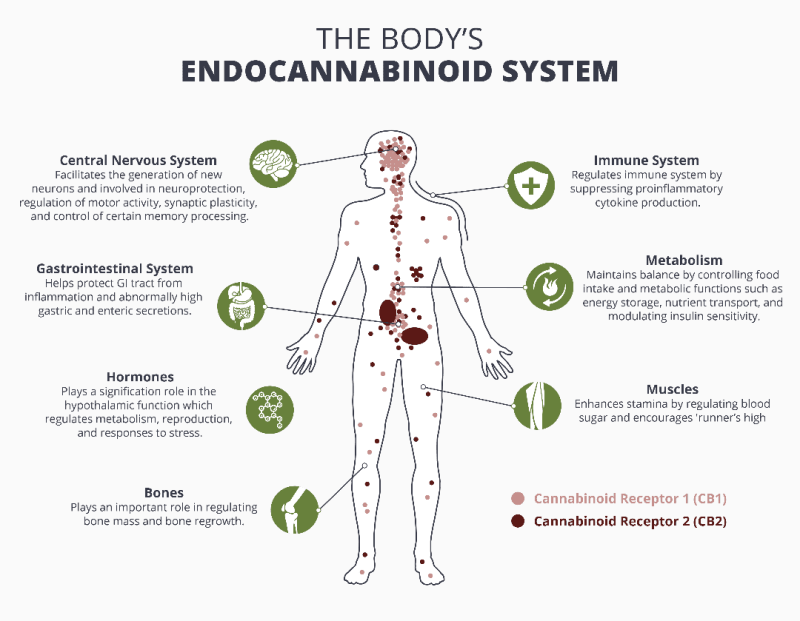
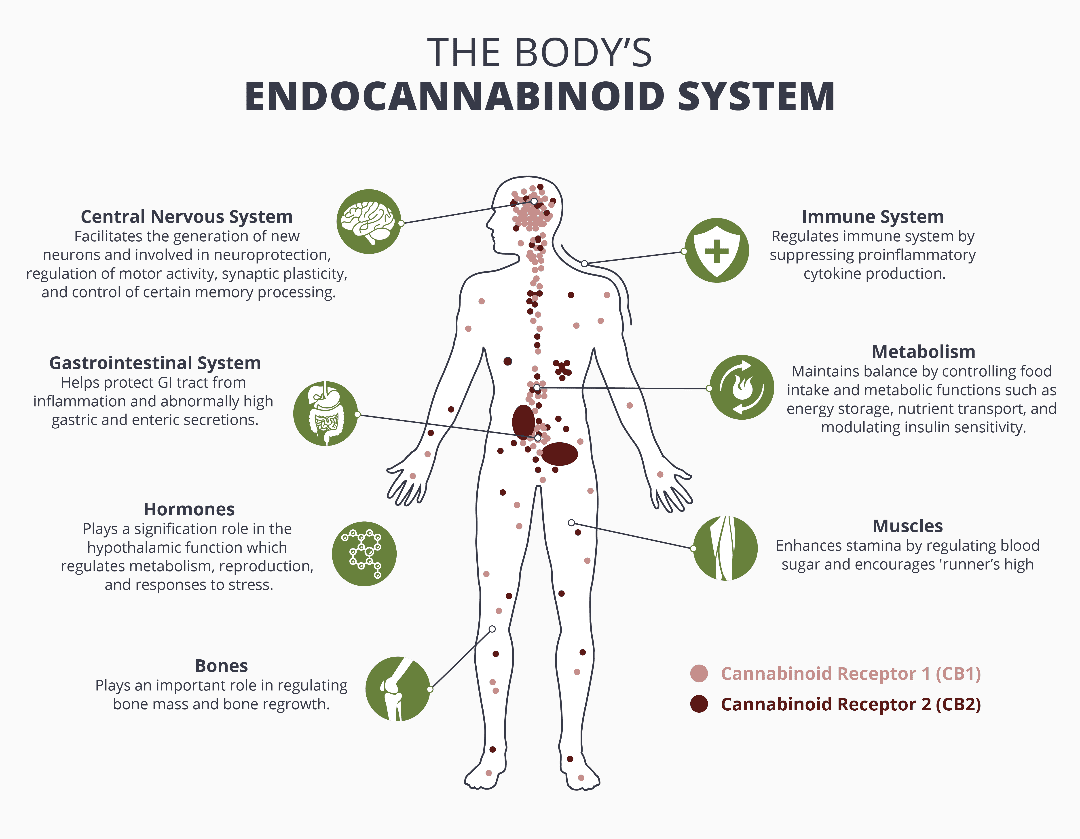
The cannabinoid interacts with the endocannabinoid system, which consists of receptors present in the brain (CB1) and immune system (CB2)
The CB1 receptor is found within the central nervous system and controls things like mood, pain sensation, appetite, and memory.
The CB2 receptor is found in the immune system and affects inflammation and pain.
Whole Hemp Extract (Full Spectrum CBD) indirectly interacts with these receptors, causing the body to produce its own endocannabinoids. This creates a positive impact on the sensations controlled by the CB1 and CB2 receptors.